Life In The Fast Lane Ecg Q Waves
If coronary heart disease is likely then infarction is the most probable cause of the q waves.
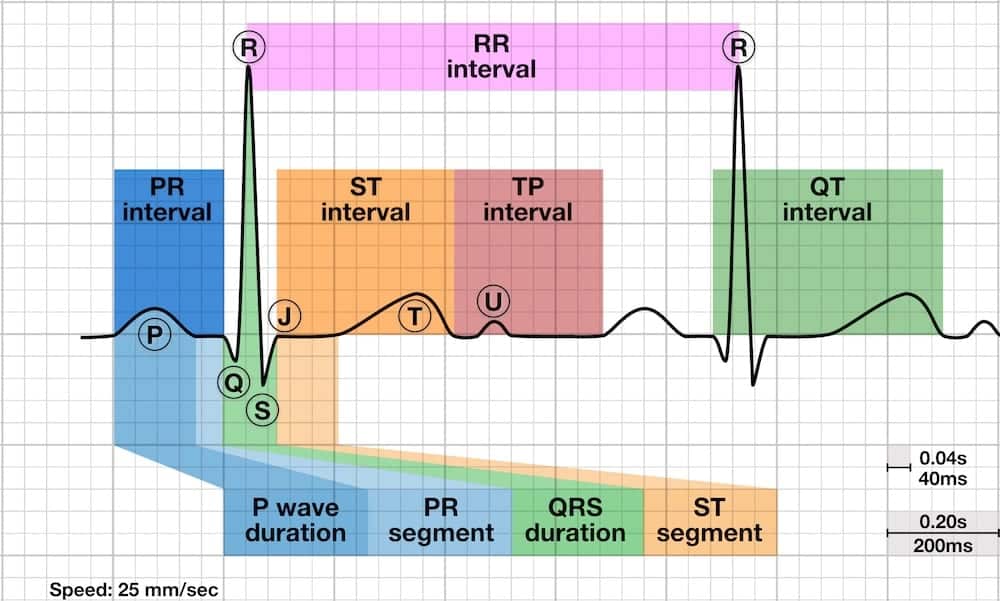
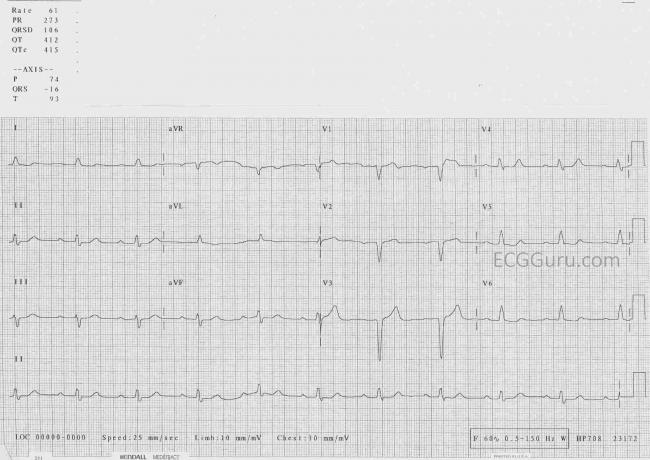
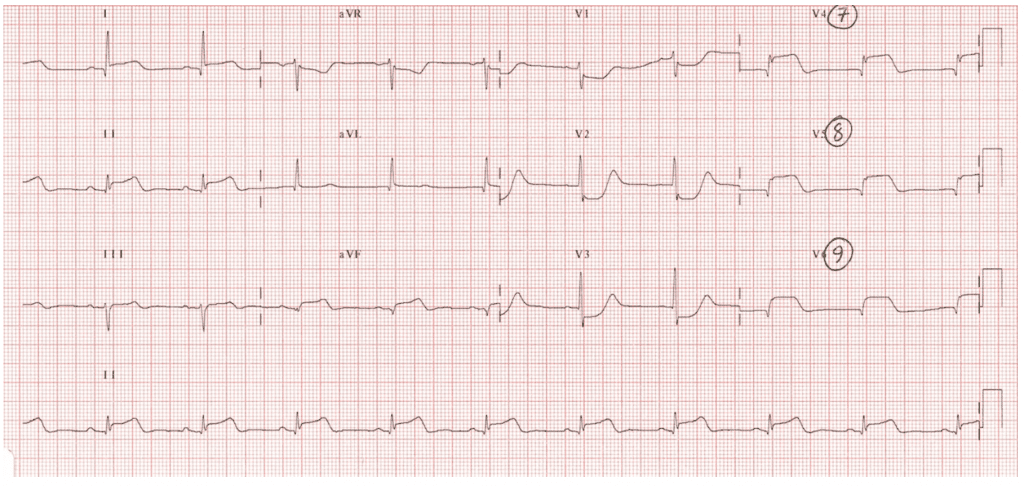
Life in the fast lane ecg q waves. Ecg changes in left ventricular hypertrophy lvh large r waves in left sided leads v5 v6 i and avl and deep s waves in right sided leads v1 v2 indicate the the vector of the left ventricle is amplified. Normal septal q wave. Small septal q waves are typically seen in the left sided leads i avl v5 and v6. Abnormal septal q wave.
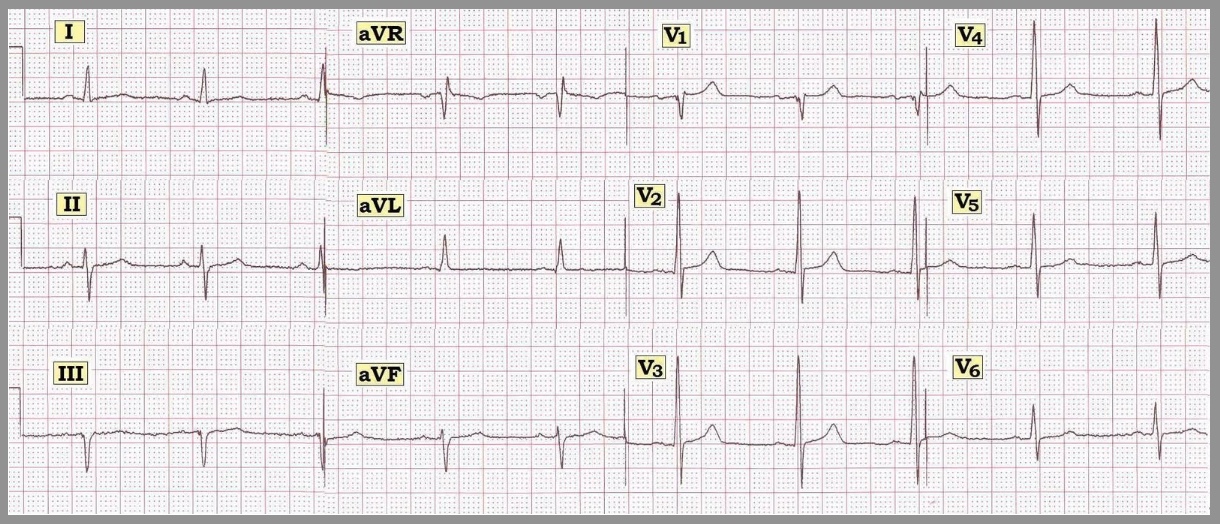
Standard textbooks have traditionally taught that the pathological q wave is a permanent ecg manifestation and that it represent transmural infarction stemi. Stage 3 flattened t waves become inverted 3 to several weeks. Stage 1 widespread ste and pr depression with reciprocal changes in avr occurs during the first two weeks. These q waves are wider and deeper than normally occurring q waves and they are referred to as pathological q waves.
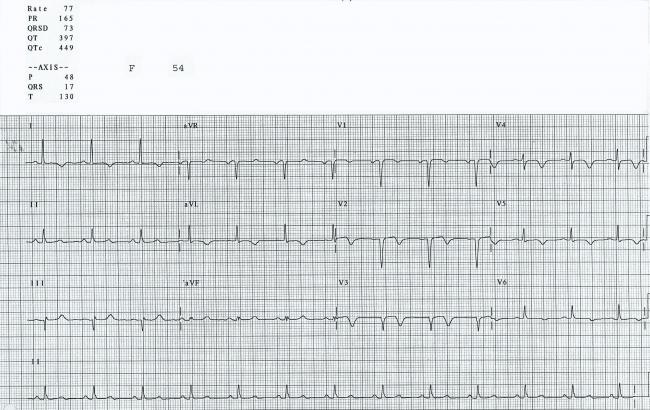
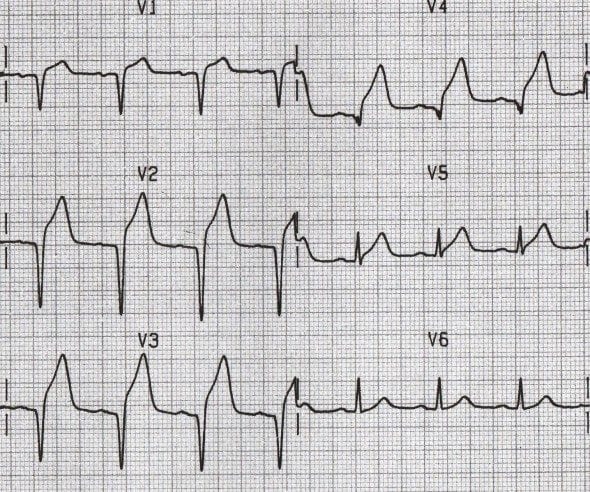
Left ventricular hypertrophy results in increased precordial voltages and non specific st segment and t wave abnormalities. Litfl ecg library is a free educational resource covering over 100 ecg topics relevant to emergency medicine and critical care. All our ecgs are free to reproduce for educational purposes provided. Ecg features of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
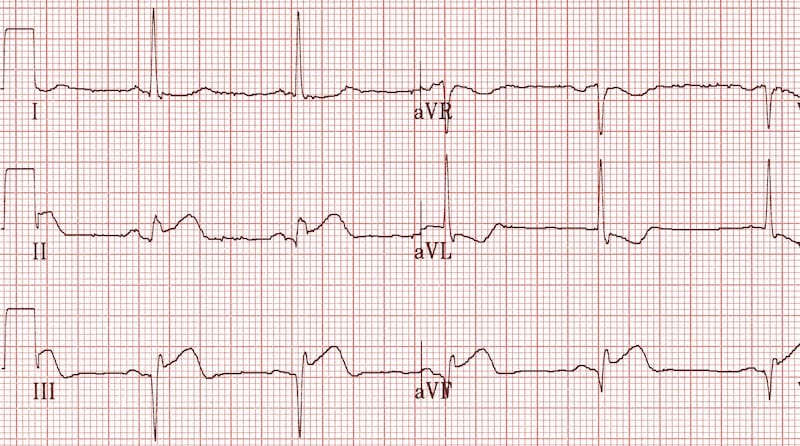
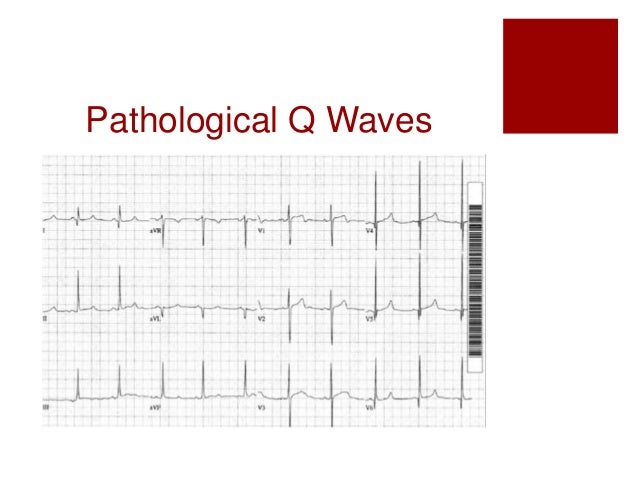
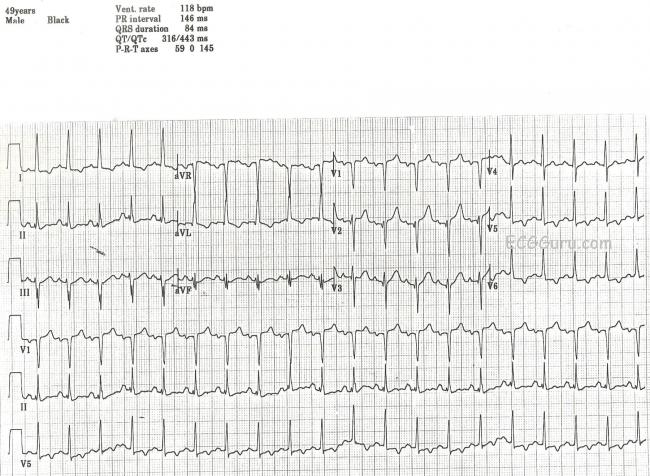
They typically emerge between 6 and 16 hours after symptom onset but may occasionally develop earlier. Arvd arvc epsilon wave f ecg bipolar precordial leads fontaine leads. 0 04s in i or in ii iii and avf or v3 v4 v5 and v6. Examples of normal and pathological q waves after acute myocardial infarction are presented in figure 12 below.
Stage 2 normalisation of st changes. Pericarditis is classically associated with ecg changes that evolve through four stages. Secondary st t changes in left sided leads left ventricular hypertrophy is often accompanied by j point depression downsloping st segment and inverted asymmetric t waves i the. Generalised t wave flattening 1 to 3 weeks.
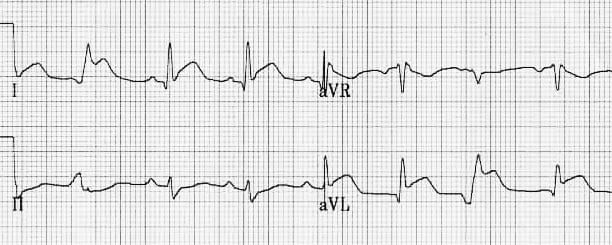
These may mimic prior myocardial infarction although the q wave morphology is. Infarction q waves are typically 40 ms. Asymmetrical septal hypertrophy produces deep narrow dagger like q waves in the lateral v5 6 i avl and inferior ii iii avf leads. The q wave represents the normal left to right depolarisation of the interventricular septum.
Must distinguish normal septal q waves from pathologic q waves. A q wave is any negative deflection that precedes an r wave. Q waves do not always indicate infarction. However recent studies challenge these notions.
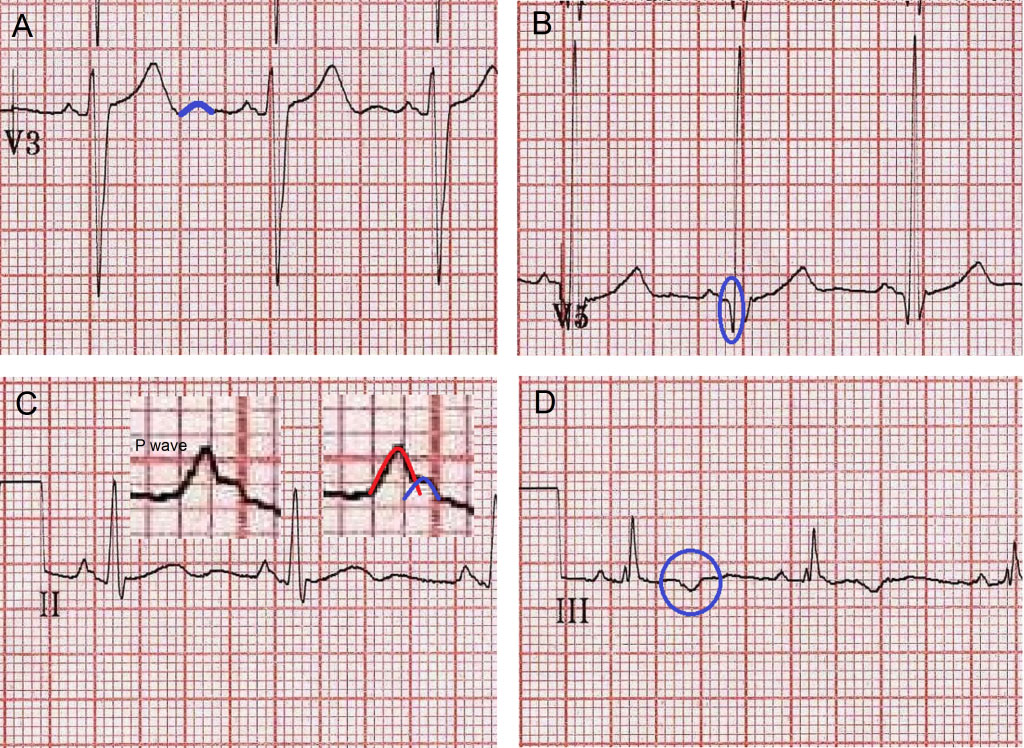
Q wave equivalents in the precordial leads.